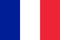
Cervical osteochondrosis is a chronic disease caused by degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs of the neck. As the disease progresses, the surrounding structures are involved in the pathological process, which causes the development of a number of unpleasant symptoms. The treatment of the disease is complex, conservative and includes taking medications and non-drug methods.
Causes
The exact reasons are not known. The theory that the development of the disease is associated with age changes has not been confirmed, as today this pathology is also diagnosed in teenagers.
Factors that can cause the development of the disease include:
- low physical activity, sedentary lifestyle;
- mechanical neck injuries;
- sedentary work with high static load on the cervical spine;
- uncomfortable mattresses and pillows;
- obesity;
- blood circulation disorders;
- scoliosis and other postural defects;
- connective tissue dysplasia;
- metabolic disorders.
Syndromes and symptoms

Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis do not appear immediately. For a long time, the disease can develop asymptomatically or be masked as other pathologies. The most common signs of cervical osteochondrosis are:
- tinnitus - usually happens when you change position after a long stay in a stationary position;
- dizziness - the patient periodically feels as if objects have begun to rotate in front of his eyes;
- pain in the neck, in the back of the head - the intensity of the pain depends on the degree of pathological changes;
- feeling of lack of air - the patient cannot take a deep breath;
- visual impairment - occurs in the later stages;
- nausea, vomiting - are also associated with impaired blood supply to certain parts of the brain due to compression of the main arteries by deformed discs;
- sore throat, dry throat, foreign body sensation;
- pressure changes that are poorly controlled by medications;
- numbness of the fingers;
- shoulder pain.
In addition to general clinical signs, several characteristic syndromes are distinguished:
Vertebral:
- pain when turning the neck;
- impaired mobility;
- X-rays show signs of damage to the vertebrae and discs.
Cardiac:
- burning and pain in the chest;
- increased fatigue, weakness without cause;
- tachycardia.
Vertebral artery. This syndrome appears as a result of narrowing of the vertebral artery, which supplies the brain with blood. It is manifested by tinnitus, dizziness and blurred vision.
Koreshkovy. It occurs due to pinching or compression of the nerve roots that exit the cervical spine.
stages
Stages of the disease:
- The patient feels slight discomfort in the neck area. Intervertebral discs begin to lose stability.
- Pain appears. The discs are deformed, the destruction of the fibrous ring begins and the vertebrae come closer together.
- Neck movements are limited. When you turn your head, nausea and dizziness may appear. The constant lack of blood in the brain leads to symptoms such as lethargy, weakness, decreased performance and fatigue. The discs become thinner, the vertebrae begin to rub against each other, the fibrous ring is destroyed and intervertebral hernias are formed.
- The neck area is immobile, the blood supply to the brain is completely cut off. To correct this condition, the patient must constantly take special medications. The beads begin to join together.
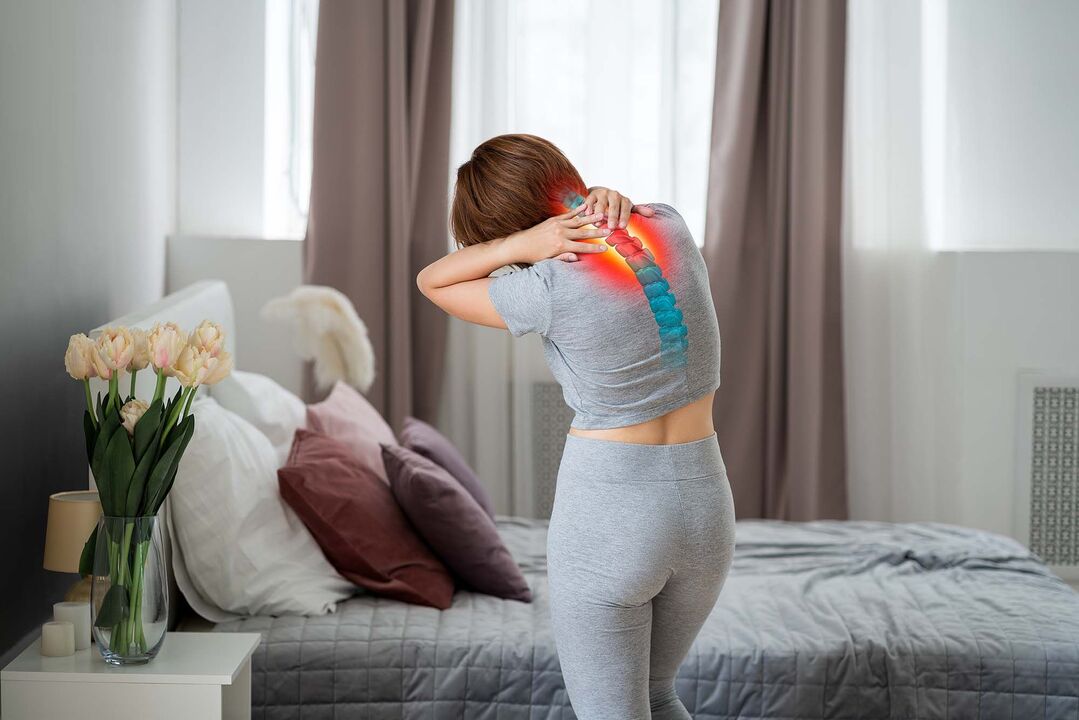
Diagnosing
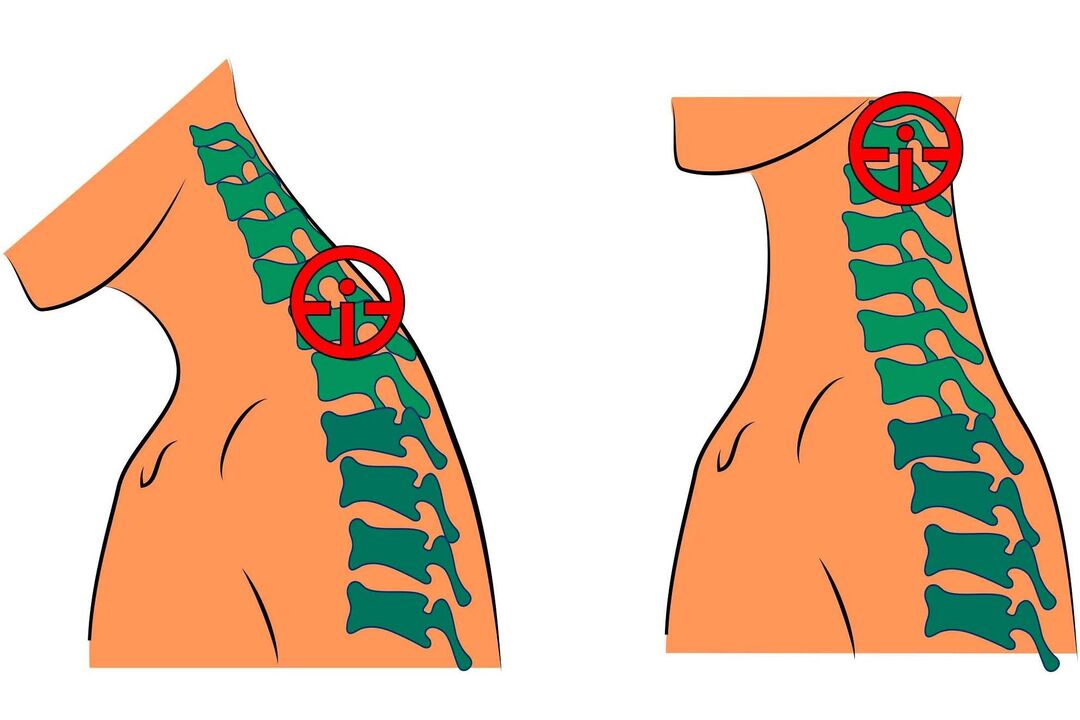
Diagnosis can be difficult due to the non-specific clinical presentation and wide variability of possible symptoms. The patient may need the help of several specialists at the same time (surgeon, neurologist, cardiologist, vertebrologist, orthopedist and others).
At the meeting, the doctor listens to the patient's complaints, collects the anamnesis, performs an examination and makes a preliminary diagnosis.
To confirm it, the following can be described:
- blood analysis;
- MRI of the neck - allows you to identify pathological changes even at the initial stage of the disease, when the clinical manifestations are not yet very pronounced; with the help of this study you can evaluate the current condition of the vertebrae, discs, identify the presence of deformations, osteophytes, compression of nerves and blood vessels;
- Dopplerography of the cervical arteries - allows you to assess the degree of compression and damage to blood vessels, the speed of blood flow;
- myelography using contrast - allows you to identify pressed nerves;
- ECG - performed for differential diagnosis with cardiovascular diseases.
Treatment
Drug therapy includes taking the following groups of drugs:
- NSAIDs. Effectively relieves inflammation, pain, swelling. These are symptomatic therapy tools that do not affect the causes of the disease. NSAIDs can be used in short courses of 10-14 days.
- Angioprotectors, means to accelerate blood flow. Improves cerebral circulation, protects blood vessels from damage.
- Glucocorticosteroids. Effectively relieves pain and nerve compression. Medicines of this group have many side effects and should be taken only according to the doctor's recommendation if NSAIDs and analgesics do not help.
- Chondroprotectors. It improves the health of the intervertebral discs, affecting the causes of the disease. They prevent the destruction of cartilage tissue and improve the shock-absorbing properties of the discs.
Treatment without drugs may include the use of the following techniques:
- Exercise therapy. Regular exercise strengthens muscles and relieves spasms. Classes (at least at the initial stage) are recommended to be conducted under the guidance of a specialist
- Manual therapy. Neck muscle spasms are one of the main causes of pain in this disease. Properly performed manual therapy helps to get rid of spasms, compression of blood vessels and nerves. As a result, nutrition of the discs improves, cerebral circulation normalizes and pain disappears.
- Kinesio taping. The application of special strips relaxes the muscles, relieves spasms, swelling, inflammation and at the same time keeps the spine in a physiologically correct position.
- Orthopedic equipment. To minimize the load on the cervical spine, it is recommended to use orthopedic mattresses and pillows for sleeping. In addition, some patients are recommended to wear a special device (Schanz collar), which fixes the neck in the right position.
- Massage. An effective drug against the cervical form of the disease. It perfectly relieves swelling, pain, congestion, improves local blood circulation, relieves muscle spasms. Do not massage if you have acute neck pain.
- Physiotherapy. Another effective technique. Sessions are held in courses, several times a year. This allows you to get rid of unpleasant symptoms, relieve muscle spasms and slow down the further progression of the disease. For the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, laser therapy, magnetic therapy, mechanotherapy, traction therapy, hydromassage, UVT and mud therapy are most often used.
If conservative therapy does not give results and the disease continues to progress, then surgical treatment may be prescribed.
- operations to remove intervertebral hernias;
- removal of the vertebral arch or spinous processes leads to decompression of the roots of the spinal cord;
- removing part of the disc's core to repair a herniated disc.
The decision on how to treat the disease is made by the doctor individually for each patient. Self-medication is prohibited and can lead to the development of a number of complications.
Complications
If the disease is neglected, the following complications may develop:
- VSD;
- brain starvation from oxygen;
- arterial hypertension;
- blurred vision, retinal dystrophy;
- respiratory spasm;
- violation of the act of swallowing due to esophageal dysfunction;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- Cramps and numbness of the neck muscles;
- chronic upper body pain that is not relieved by analgesics;
- hormonal imbalances.
Preventing
To minimize the risk of developing the disease, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- take the stand;
- properly equip the workplace so that neck strain does not occur;
- Healthy food;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- avoid neck injuries;
- move more, exercise;
- don't get too cold;
- control weight;
- sleep on a special orthopedic mattress and pillow;
- do gymnastics regularly to avoid the development of overload;
- prevention of curvature of the spine;
- regularly undergo massage courses to improve blood flow and relieve congestion;
- do not sit for a long time in a position with the head bent forward;
- If you have discomfort in the neck area, you should make an appointment with a specialist and undergo an examination; this will help identify possible changes in the discs at an early stage, which will greatly facilitate treatment and improve the prognosis.